The livestock industry has undergone many significant changes over the last three centuries.
For example, in a few decades, we’ve gone from simple ploughs to microchip-controlled tractors that can make semi-autonomous task-based decisions.
And we’re on the verge of adopting smart tractors that take intelligent decisions, informed by AI, based on the needs of the farm with little human intervention.
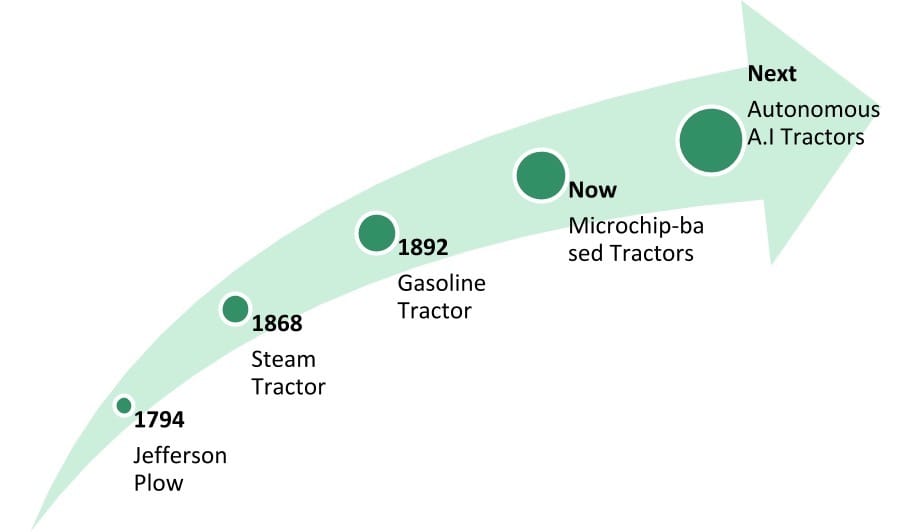
But what’s this got to do with the next leap in livestock farming?
There’s a common connecting thread.
Like all the previous leaps in farm technologies so far, the next leap in livestock farming also promises greater productivity gains and reduced manual effort.
In this article, let’s look at the role of a few digital technologies that are on the verge of helping progressive livestock farmers keep pace with market demands. Read this to understand what these digital technologies can offer.
Livestock Farming Technologies
Over the past decade, predicting, tracking and managing livestock has undoubtedly become easier and more accurate with advances in technology.
As we speak, several self-learning algorithms are being developed and refined to help livestock farmers to collect data and monitor various aspects of their farm continuously.
These smart decision support tools help farmers make informed and proactive decisions before any problem gets out of hand.
These technologies also promise to improve growth, production, animal performance and profits.
But more importantly, such as Digital Technologies can help progressive farmers scale up their operations and compete more efficiently in an increasingly global marketplace.
Why is Technology Important?
Across the world, the livestock sector is facing several significant challenges.
On the one hand, there is increased demand for milk, meat and other livestock products. And then there is more pressure on livestock farmers to lower greenhouse gas emissions, improve animal welfare and do all this with fewer resources.
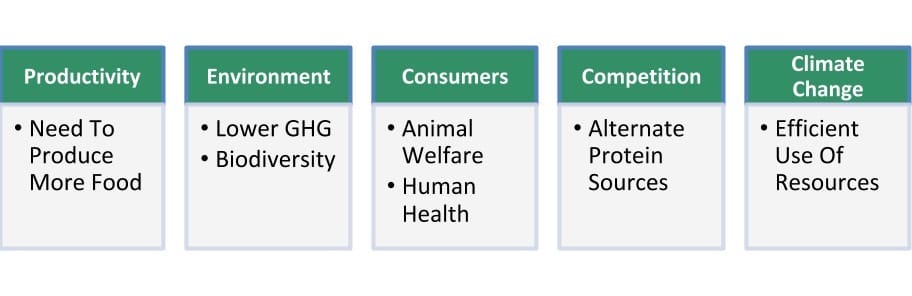
Current livestock farm management practices are insufficient to meet all these challenges.
Furthermore, the next wave of growth and gains in the livestock sector are all estimated to come from adopting new technologies.
For example, in Australia, it is estimated that gross production of agriculture could increase by $20 billion (relative to 2014/15) as a result of adopting new digital technologies.
The biggest challenge today is that livestock farmers are increasingly being pushed to DO MORE with LESS. This is where digital technologies that use data to optimize farming processes and operations can add a lot of value.
This is a huge opportunity for livestock farmers, especially if you consider that livestock production makes about half of Australia’s $30 billion annual agricultural productions today.
Six Smart Technologies You Should Know About
When we refer to Digital Technologies, some examples that come to the top of our minds are:
- Smart Satellite & Drone Services: That use a range of sensors and multi-spectrum images from above to monitor crops, pastures and grazing fields closely. To transmit location, health, population and biomass information back to the farmers.
- Smart Infrastructure Systems: That use a range of sensors to detect changes in the environment and automatically adjust lighting, ventilation, cooling and airflow systems to meet the needs of animals. Also allows farmers to make changes remotely.
- Smart Animal Welfare Systems: That make use of several sensors, wearables, probes and imaging technologies to capture real-time information about key animal welfare parameters constantly. And helps farmers to identify and resolve problems through remote devices.
Let’s take a closer look at SIX of the Key Technologies that are currently impacting Livestock Farming.
I will help you understand what each technology actually is, how they work, and how you, as a livestock farmer can use them to reap benefits.

1) Precision Agriculture (PA)
What is PA?
Precision agriculture makes use of satellites, sensors and other connected devices to understand key changes in the farm and helps farmers make better decisions that solve the root problems.
For example, pasture fields might be suffering from lack of irrigation. A combination of satellite-based pasture growth measurement can help farmers identify this problem even before the drop in per ha yields become evident to the human eye.
How does it work?
As discussed, to help farmers make better decisions, PA typically makes use of several technologies that include a vast array of tools of hardware, software and equipment.
For example, some of them might be:
- Global Positioning System (GPS) and Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) receivers
- Geographic information systems (GIS)
- Remote sensing tools
- Variable Rate/ Growth Software Applications
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Algorithms
How does it apply to Livestock Farming?
- allows close pasture and livestock monitoring
- informs about soil and irrigation conditions
- can warn about pest attacks, lack of drainage and low growth
- can track key soil parameters and in turn increase yields
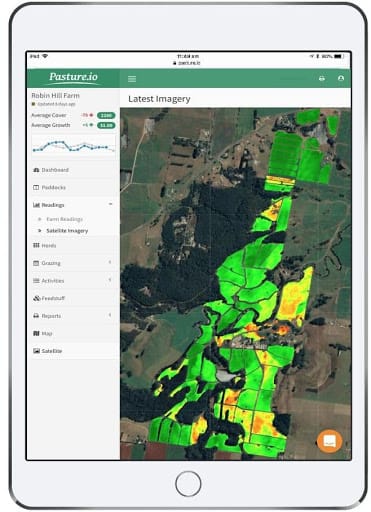
2) Big Data
What is Big Data?
As you can imagine, continuous collection of real-time data over time will result in large volumes of data that go beyond the capacities of conventional computers and software applications.
A specific set of technologies that can store, handle, process and analyze such large volumes of data is collectively known as Big Data.
How does it work?
Stores and processes the data captured by a href="https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/sustainability/assets/ai-for-the-earth-jan-2018.pdf" | millions of sensors | used to monitor farm assets, animals and equipment. The data is then formatted and analyzed into actionable outcomes.
How does it apply to Livestock Farming?
Big Data applications in Smart Farming is influencing the entire a href="https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/food-supply-chain" | food supply chain |.
Big Data applications might include benchmarking, sensor analytics and predictive modelling to manage crop failure risk or even boost feed efficiencies in livestock production.
Examples of Big Data applications:
Biometric sensing, GPS tracking of Livestock movements
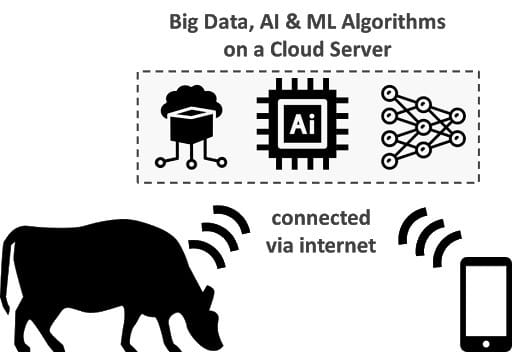
3) The Internet of Things (IoT) Or Rather the Internet of Animals
What is IoT?
The Internet of things (IoT) is a system of unique devices that can relate, communicate and transfer data with each other via a connected network without requiring significant human interaction.
How does it work?
Once sensors are installed throughout the fields, agriculture vehicles and local weather stations – they will begin to collect and transmit data to the farmer’s monitoring systems (computers or smartphones) in real-time.
How does it apply to Livestock Farming?
IoT is used in smart agriculture for information on soil, humidity, moisture, light, air temperature, CO2, solar energy sensor.
IoT devices are used in farm recordkeeping, field management, inventory, operations, grazing and biosecurity.
Example:
Livestock Feeding and Milk Maximizing- Farmers track herd behaviours like feeding with the IoT device, closely monitor herd movement (grazing, reproduction or chewing cud). This data collected via sensors built within a wearable around the cow's neck can help increase milk production, allowing cows to be milked several times a day at a favourable time.
4) Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) And Robotics
What is AI? What is meant by Robotics?
Simply put, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can be thought of intelligent machines that are capable of taking independent decisions based on evidence it collects.
And robotics is the use of robots to perform human tasks such as carrying loads, milking cows and seeding pastures.
How does it work?
Computer algorithms are trained to analyze a few key parameters and metrics and over time, uses this information to improve data-based decision-making.
How does it apply to Livestock Farming?
AI has emerged as a tool that empowers farmers in monitoring, forecasting, as well as optimizing the farm animal growth. It helps to tackle parasites, biosecurity, and diseases.
Example:
Automated milking robots, control and milk cows with high speed, while they consume their feed via sensor-controlled mechanical arms.

5) Blockchain
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is a structure that stores transactional records, also known as the block, of the public in several databases, known as the “chain,” in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes.
How does it work?
Blockchain is a combination of three leading technologies:
- Cryptographic keys that help validate transactions between two parties via secure digital identities.
- A peer-to-peer network containing a shared ledger
- A means of computing, to store the transactions and records of the network
How does it apply to Livestock Farming?
Farmers in the near future may begin to interact with Blockchain-based technologies via smartphones and personal computers, without even realizing it.
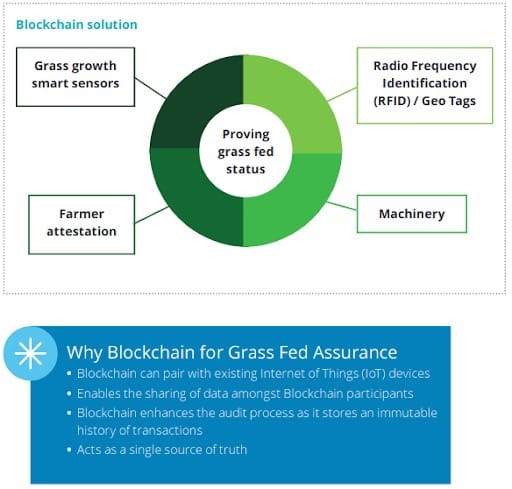
Blockchain has the potential to connect the entire supply chain from producer to consumer and help food traceability and safety.
It can give farmers complete transparency and a competitive advantage. It may be used to:
- Perform quality control and audits
- Trace every animal product at every stage of the supply chain
- Track all the ingredients with respect to its source
Example:
Blockchain can allow consumers to verify that their produce meets specific growing standards reliably.
The most prominent example in this area is Deloitte's Grass-Fed Assurance program in Ireland.
6) Augmented reality (AR) and Virtual reality (VR)
What are AR and VR?
Augmented reality (AR) can be defined as the integration of digital information with the user's environment in real-time. AR alters the surroundings by adding 3D objects, sounds, videos, graphics to it.
Virtual reality (VR), on the other hand, is defined as a digital environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real way through electronic equipment, shutting out the physical world.
How do they work?
AR uses computer vision, simultaneous localization, mapping and depth tracking (sensor data calculating the distance to the objects) to collect, send and process data to show digital content relevant to the user.
The VR headset puts up a screen (or two – one for each eye) in front of eyes thus, eliminating any interaction with the real world. The visuals on the screen are rendered either by using a mobile phone or HDMI cable connected to a PC.
Examples:
AR can allow a farmer to immediately see stats relating to the farm through the use of goggles. Information relating to each cow is sent through the glasses into the farmer’s field of vision. They can see information on everything in the facility and even evaluate milk quality.

New Zealand has partnered to develop a virtual reality health and safety training technology that allows employees to navigate the manufacturing and distribution sites, using goggles, without actually setting foot on the physical site, thus reducing onboarding times.
What all this means for you
I hope that this gave you a sneak peek into the upcoming digital technologies that might help you optimize your livestock farm business in the near future.
Look out for advances in these digital technologies, as they might help you manage production risks and improve your productivity.
In case you found this useful, you might also be interested in what we have to offer.
Pasture.io helps you put your pasture measurements on autopilot and make effective grazing decisions.
Our farmers have received up to a 40x return on their investment with us.
Please check out our free and paid plans. It might change your life and your pasture for the better.
Happy farming!
- The Dedicated Team of Pasture.io, 2020-08-28