Article Summary:
Being a farmer is not everyone’s forte. It requires flexibility, persistence, and tactical grazing management to meet your growth targets and keep the pasture flourishing and profitable. Learn to switch between different grazing practices, make informed decisions, and meet your growth targets with our guide on tactical grazing management.
Pastures are at the base of grazing systems across the world. Managing pastures throughout the year requires tactful management and informed decision making.
Tactical grazing management is just that; a flexible grazing management system that keeps the track of livestock demand, pasture’s capacity along with seasonal changes when drawing grazing management decisions.
Tactical Farm managers such as yourself are using smart approaches to perform management tasks efficiently. They systematically keep;
- Pasture utilization at its highest level
- Ensuring their ground cover targets are met
- Track of seasonal feed budget
- Pasture targets and capacity in consideration
- Record of the previous grazing plans and incorporate them into future decision making.
Today, we will discuss what tactical grazing management ought to achieve and define its objectives. We will formulate management strategies farms can switch between according to season and growth targets. Finally, we will break down tactics for specific conditions. There are a lot of takeaways for you dear farmer, let’s get started.

Aims of tactical grazing management: A win-win for pasture and pasture management
Our aim behind adopting tactics is to make the most of what pasture has to offer. To that end, we tirelessly investigate, experiment, and finally discover ways that best fit every unique farm. Tactical grazing management offers the following benefits.
- It aims to reduce the cost of production
- Promotes the growth of crops
- Hinders the growth of weeds
- Effectively increase the stocking rate
- Maximises pasture utilization
- Optimises pasture productivity and perseverance
- Boosts the production of livestock
- Increase the efficiency of feed conversion
- Move toward sustainable pasture management by reducing the harmful environmental impacts such as waterlogging, erosion, salinity, and reduction in nutrient value.
Keeping in mind all these achievable aims make tactical grazing management a panacea to the various pasture troubles. Farms across Australia use a mix of methods to ensure their pasture management is up to the mark. Without further ado, we delve into the ways of grasping tactical management!
1. Maximise pasture utilisation
Set a rotational grazing system by incorporating time and pasture growth, paddock division and subdivision, stocking rates and calving times. Know that the best time for rotational grazing is all year round, which makes things easier ;-)
Also, apply a rotational grazing system in a way to avoid selective or patch grazing. Stop using in case of compromised animal growth like during the time of lambing.
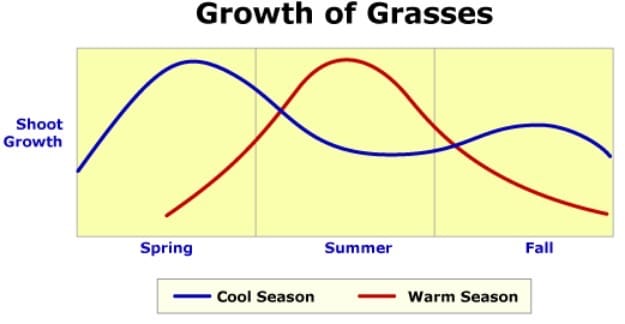
2. Enhance pasture growth
Rotational grazing when based on plant growth has the potential of increasing pasture growth up to a swooping 20%. Calculating kg of dry matter/ha, plant height and leaf stage help in setting tactical rotational grazing systems.
Set rotational grazing throughout the year for perennial and to produce long term impact on pasture composition. You can also use rotational grazing to achieve pasture growth for a specific season like winter.
3. Control and manage stock intake
To efficiently manage and control the stock intake(kg dry matter/ha/ day), set rotational grazing system on criteria of animal intake during critical periods like pregnancy or all year long in case of growing bulls for beef.

4. Evaluate and ensure specific livestock management needs
Utilize flexibility when choosing between set stocking or rotational grazing. Set stocking works better for lambs and for managing single sire mating. It is also effective for controlling diseases like footrot or any other outbreak.
On the other hand, rotational grazing is more effective when it comes to evaluating and monitoring livestock performance regularly and for controlling internal parasites.
Therefore, it is recommended to choose a combination of both grazing methods according to the specific pasture goals and set targets.
5. Optimise pasture composition
There can be four different approaches to optimise pasture composition;
- To produce more perennial grass: rotational grazing system has a lot to offer if the aim is to increase the perennial grass content. When rotational grazing is based on time or plant growth stages it reduces the growth chances for broadleaf weeds and annual grasses. By choosing a rotational grazing system you can tactically lay it for rest over the summer.
- To lead to high sub-clover content: Increasing grazing pressure and reducing the rest period for late winter/early spring under rotational grazing can lead to an increase in the sub-clover ratio. However, there are increased chances of broadleaf weed growth. Stock grazing can also be utilized.
- To minimize annual grasses and weeds: By setting the pasture to rest over the winter helps minimize tillering and minimises the annual grasses and weeds.
- To manage woodland thickening: controlled and well-planned burning after considering the seasonal conditions.
6. Increase persistence of perennials
It is tactical to use the rotational grazing system for perennials. The period of rest between grazings is crucial for growth and persistence as perennial grasses rebuild their root reserves. The seed selection process is of the essence when planting perennial grasses.
needs to be taken in case of less drought-resistant perennial grasses such as cocksfoot and perennial ryegrass. They need to be put to rest in a dry/warm season or not grazed extensively.
7. Enhance environmental sustainability
A tactical grazing system addresses the need for environmental sustainability. A rotational grazing system designed to maximize the perennial content while efficiently utilizing water, meeting the targets of ground cover fulfils the criteria of environmental sustainability.
Set stocking can also be sustainable given a low stocking rate, homogeneous typography, and low erosion risk.
Bonus point:Occasional set stocking to meet some other production objectives would not compromise the sustainability of the rotational grazing system. Be sure to use this flexibility to your vantage.
Tactical grazing management is a win-win for pasture productivity and management. It has the potential of producing more gains and returns from efficient planning and management.
Tactical management can significantly increase farm profitability by perfecting the grazing management processes. This brings us to the end of the article.
Until we meet again, Happy Tactical Grazing!
- The Dedicated Team of Pasture.io, 2021-11-24